Compression springs are used in a variety of mechanical applications to provide the force needed to compress a spring-loaded product. Compression springs are typically made from steel but can also be made from other materials such as stainless steel, titanium and aluminum. The design of a compression spring is dependent upon two main factors: the load it must handle and its end use application.
Compression springs provide the force to compress a spring-loaded product.
Compression springs are used in a variety of applications, including the automotive industry, medical devices and consumer products. Compression springs provide the force to compress a spring-loaded product.
Compression springs are typically made up of wire that has been wound around itself in order to form an enclosed loop. When compressed, this coil will straighten out into its original shape while also applying pressure against its surroundings. This allows it to move objects or other pieces of metal without having any additional support outside of its own structure (as opposed to tension springs).
Material selection for compression springs is based on spring load and application.
Material selection for compression springs is based on spring load and application. Compression springs are manufactured from a variety of materials, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Material selection will depend on the type of compression spring being designed, as well as its load capacity, operating temperature range and service life requirements. The three most common types are steel (carbon or stainless), nickel alloy and cold-rolled steel wire.
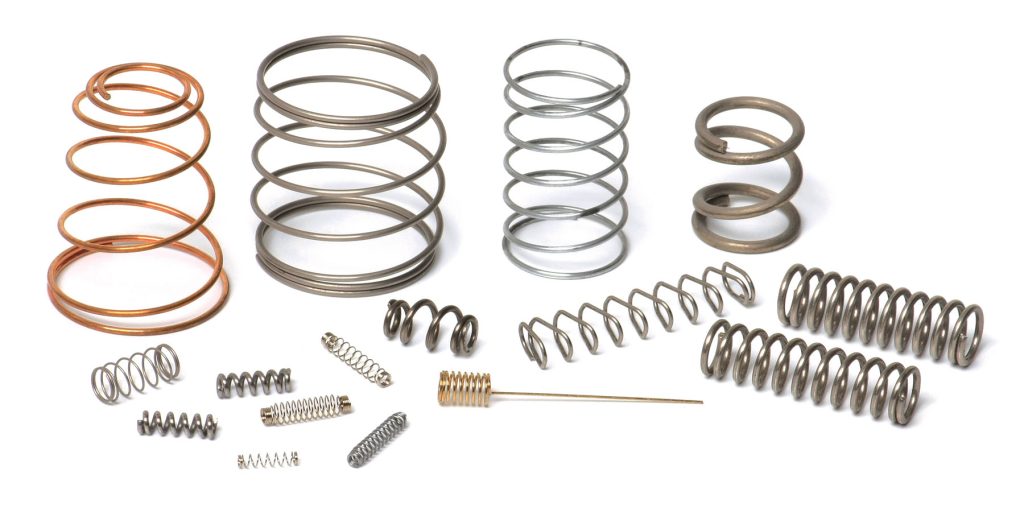

The design of a compression spring includes consideration for its ability to handle stress.
The design of a compression spring includes consideration for its ability to handle stress. Stress is defined as force per unit area, and it’s important to consider how much stress your application can tolerate before failure occurs. The amount of force needed to compress a given distance from rest (called spring load) depends on many factors:
- The material and design of the spring
- The application and environment where it will be used
There are multiple types of compression springs, including flat wire, torsion and helical.
The most common type of compression spring is the flat wire design. Flat wire springs are used in applications where force is applied to the outer surface of a cylindrical coil, such as when you press down on your car’s accelerator pedal. Flat wire springs can also be used in situations where there may be an axial load (force applied along an axis), such as holding something up or securing it against pressure from another direction.
Torsion springs are designed to resist torque (rotating) motion rather than linear force or tension, which makes them useful for applications like door locks and window shades that need to rotate but not stretch out over time due to constant use or wear-and-tear effects like fatigue failure modes or creep deformation mechanisms inside metal alloys that make up parts like these ones!
Selecting the right compression spring is dependent upon your application needs.
Compression springs are used in a wide range of applications. The most common uses include:
- Mechanical engineering (e.g., automotive and industrial)
- Electrical engineering (e.g., appliances, computers, and electronic devices)
- Medical devices (e.g., medical equipment)
There are many factors to consider when selecting the right compression spring for your application needs. These include material selection, design considerations, and application needs.
Compression springs are an essential part of many products and devices. They are used in everything from clocks to medical devices and even cars. There are many factors to consider when selecting the right compression spring for your application, including material selection, load capacity and design considerations. The most important thing is to make sure that the spring will work well with what you need it for!

